The landscape of cloud hosting has become integral to modern digital infrastructure, offering unprecedented flexibility and scalability. However, the financial dynamics associated with cloud hosting can be intricate and require a nuanced understanding. This article aims to unravel the multifaceted elements contributing to cloud hosting costs, providing a detailed exploration to empower businesses in navigating this complex terrain.
Categories of Cloud Hosting Models
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service allows users to rent virtualized computing resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. Costs encompass virtual machines (VMs), storage, and data transfer.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service provides a pre-configured platform, ideal for developers. Costs include application hosting, databases, and development tools.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service delivers software applications over the internet. Costs involve licensing fees, user subscriptions, and customization.
Factors Driving Cloud Hosting Costs
1. Resource Utilization
The direct impact of CPU, RAM, and storage on costs. Optimizing resource usage is crucial to align with application requirements.
2. Storage Expenses
Varied costs for different storage types (e.g., Standard, SSD). Consider redundancy options and select appropriate storage tiers.
3. Data Transfer Charges
Ingress and egress data transfer contribute to costs. Optimizing data transfer using content delivery networks (CDNs) can be a strategic move.
4. Geographical Impact
Different rates based on the physical location of resources. Choosing data center locations strategically can optimize costs.
5. Instance Varieties
Different costs associated with various VM instance types. Matching instance types with workload requirements ensures cost efficiency.
6. Reserved vs. On-Demand Instances
Reserved instances offer savings for predictable workloads, while on-demand instances provide flexibility but at a higher cost.
7. Scaling Tactics
Auto-scaling and load balancing affect costs. Designing scalable architectures is essential for efficiently handling variable workloads.
8. Monitoring and Management Tool Costs
Additional costs for advanced monitoring and management features. Evaluating the necessity based on the complexity of your application is crucial.
Hidden Expenses and Considerations
1. Downtime Implications
Factoring in costs associated with potential downtime is crucial. Implementing high availability and disaster recovery measures can mitigate these costs.
2. Licensing Fees
Some software licenses may incur additional expenses in the cloud. Verifying licensing terms and costs for third-party applications is essential.
3. Support Tiers
Premium support options can significantly impact costs. Assessing your support needs and choosing an appropriate support tier is a critical decision.
4. Security and Compliance Costs
Robust security measures and compliance adherence may involve additional expenses. Including costs related to security services and compliance tools in your budget is essential.
Strategies for Cost Optimization
1. Rightsizing Resources
Regularly assessing and adjusting resource allocations based on actual needs is crucial. Implementing automated tools for continuous optimization can be advantageous.
2. Reserved Capacity Planning
Leveraging reserved instances for steady-state workloads and planning reservations strategically based on usage patterns is a prudent approach.
3. Usage Monitoring
Utilizing cloud provider monitoring tools to identify underutilized resources and setting up alerts for detecting unusual usage patterns can contribute to cost optimization.
4. Containerization and Serverless Architectures
Exploring containerization and serverless options for cost-efficient scaling and optimizing costs by paying only for actual resource consumption can be transformative.
Cloud Hosting Costs from Popular Providers
Cloud hosting costs can vary widely based on factors such as the cloud service provider, specific services utilized, resource configurations, and usage patterns. Here are examples of cloud hosting costs from popular providers:
1. CyberHosting
CyberHosting, the epitome of speed and simplicity, brings LiteSpeed Websites to the forefront of your hosting experience. Designed exclusively for LiteSpeed web servers, CyberHosting provides a seamless platform for your next project. With a focus on performance, security, and ease of use, it’s a hosting solution that’s both powerful and user-friendly.
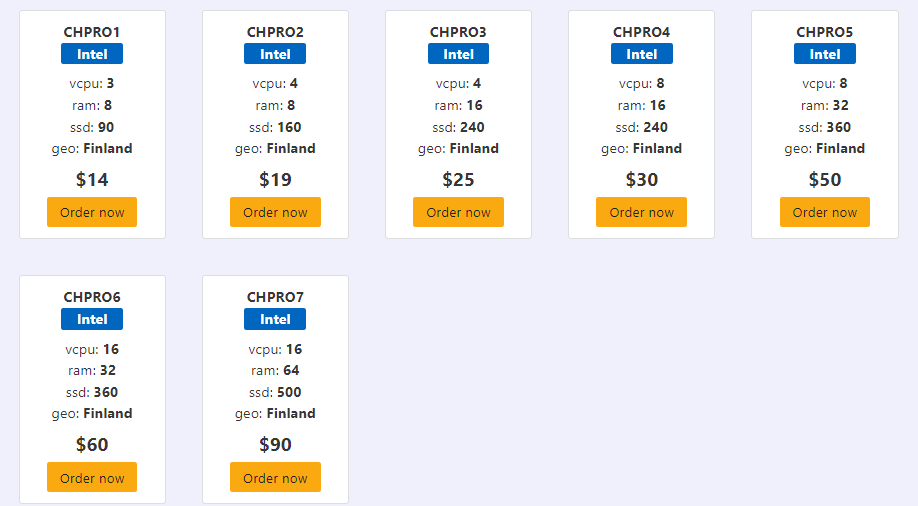
Cost Breakdown
You can check the details here.
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)

AWS provides a comprehensive range of services, including IaaS (EC2 for virtual machines, S3 for storage), PaaS (Elastic Beanstalk for application deployment), and SaaS (Amazon WorkMail for email).
A startup chooses AWS for its scalability, utilizing EC2 instances for web hosting, S3 for storing multimedia files, and AWS Lambda for serverless functions.
Cost Breakdown
- EC2 (Virtual Machines): $0.065 per hour for a t2.micro instance.
- S3 (Storage): $0.023 per GB for standard storage.
- Data Transfer: $0.09 per GB for data transfer out to the internet.
2. Microsoft Azure

Azure offers IaaS (Virtual Machines, Azure Blob Storage), PaaS (Azure App Service for web apps), and SaaS (Microsoft 365 for productivity).
An enterprise migrates its on-premises infrastructure to Azure, leveraging Virtual Machines to host applications, Azure SQL Database for data management, and Azure DevOps for continuous integration.
Cost Breakdown
- Azure Virtual Machines: $0.0184 per hour for a B1ls instance.
- Azure Blob Storage: $0.0184 per GB for cool access tier.
- Azure Data Transfer: $0.087 per GB for data transfer out to the internet.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP provides IaaS (Compute Engine, Cloud Storage), PaaS (App Engine for app development), and SaaS (G Suite for collaboration).
A machine learning startup utilizes GCP for its AI capabilities, utilizing Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) for container orchestration and BigQuery for data analysis.
Cost Breakdown
- Compute Engine: $0.0475 per hour for an e2-micro instance.
- Cloud Storage: $0.020 per GB for standard storage.
- Data Transfer: $0.12 per GB for data transfer out to the internet.
4. IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud offers IaaS (IBM Virtual Servers), PaaS (IBM Cloud Foundry for application deployment), and SaaS (Watson Studio for AI).
A financial institution chooses IBM Cloud for its security features, deploying virtual servers for critical financial applications and utilizing IBM Watson for AI-driven analytics.
Cost Breakdown
- Droplets (Virtual Machines): $5 per month for a Basic Droplet.
- Block Storage: $0.10 per GB for additional storage.
- Data Transfer: Included in the package; additional charges for excess usage.
5. Oracle Cloud
Oracle Cloud provides IaaS (Oracle Compute), PaaS (Oracle Cloud Applications), and SaaS (Oracle Fusion ERP for enterprise resource planning).
An e-commerce company opts for Oracle Cloud, leveraging Oracle Database Cloud Service for data storage and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) for scalable computing power.
Cost Breakdown
- Dynos (Containers): Free for a single dyno, additional costs for more resources.
- PostgreSQL (Managed Database): Free for hobby-tier databases, additional costs for production-level databases.
- Add-ons (e.g., Redis, SendGrid): Variable costs based on usage.
FAQs
How is data transfer calculated in cloud hosting costs?
Data transfer costs are calculated based on the amount of data moved in and out of the cloud infrastructure. Both incoming (ingress) and outgoing (egress) data transfer can contribute to costs, and pricing may vary depending on the cloud provider.
What is the significance of instance types in cloud hosting costs?
Different virtual machine (instance) types come with varying costs based on their configurations (e.g., CPU, memory). Choosing the right instance type for your workload is crucial for optimizing costs and performance.
How can one optimize cloud hosting costs?
Cost optimization strategies include rightsizing resources, leveraging reserved instances for steady workloads, continuous monitoring, using containerization or serverless architectures, and selecting appropriate storage options based on data access patterns.
What is the impact of geographic location on cloud hosting costs?
Cloud providers charge different rates based on the physical location of servers. Selecting data centers strategically can impact costs, and businesses should balance performance requirements with cost considerations.
How can businesses estimate cloud hosting costs for their specific needs?
Most cloud providers offer pricing calculators on their websites. Users can input details such as resource requirements, storage, and data transfer to get an estimate. Additionally, conducting a thorough analysis of usage patterns is crucial for accurate cost projections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, comprehending cloud hosting costs requires a multifaceted approach. By dissecting resource utilization, understanding infrastructure choices, and implementing optimization strategies, businesses can make informed decisions aligned with both budgetary constraints and performance requirements. As the cloud hosting landscape continues to evolve, the key to effective cost management lies in continuous evaluation and optimization.
Follow CyberHosting on Facebook / Twitter / Linkedin for updates.
If you want to get rid of the hosting and server issues checkout our plans in the USA. Other plans are also available in our pricing page.
